Mapping sedentary behaviour (MAPS-B) in winter and spring using wearable sensors, indoor positioning systems, and diaries in older adults who are pre-frail and frail: A feasibility longitudinal study
June 7, 2024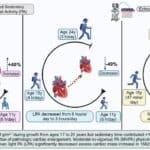
Re-post: Childhood sedentariness linked to premature heart damage – light physical activity reversed the risk
June 20, 2024A new study entitled, “Parent–Child Associations in Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: The FAMIPASS Study” was published in Children. A summary and citation are included below.
ABSTRACT
Parent–child patterns in objectively measured movement behaviours were the highlight of this study. A total of 381 families (337 mothers, 256 fathers, 190 daughters, and 191 sons) from 36 randomly selected schools and kindergartens provided valid accelerometer data. Sedentary behaviour and physical activity (PA) were assessed using ActiGraph accelerometers. Spearman’s rho was used to evaluate parent–child associations, while logistic regression analysis (the backward LR method) was used to recognize factors related to children’s achievement of PA recommendations. Results indicated that girls engaged more in light PA, while boys showed higher levels of moderate and vigorous PA. Mothers spent less time sitting and more time in light PA compared to fathers, resulting in higher total PA levels. Father–son pairs showed a stronger association in total PA than mother–son pairs. Children aged 6–10 years and those with mothers who engaged in more vigorous PA were more likely to meet PA recommendations compared to younger children and those with less active mothers.
CITATION
Sigmundová, D., Voráčová, J., Dygrýn, J., Vorlíček, M., & Sigmund, E. (2024). Parent–Child Associations in Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: The FAMIPASS Study. Children, 11(710), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11060710
Photo by Kamaji Ogino on pexels